Robotic welding torches with integrated wire brake are designed for use in robotic welding applications utilizing the weld wire to touch sense weldment parts (i.e. check for part placement and/or fit up).
When robotic welding torches are used for wire tactile sense applications, the weld wire has the tendency to move in and out of the contact tip due to robot articulation, which causes the weld torch cable to twist and turn, thereby increasing or shortening its length. However, the weld wire must be held stationary to provide accurate measurement feedback.
The addition of a wire brake will prevent the weld wire from moving by applying holding force to the weld wire during touch sense routines. The brake device is deactivated during the weld process.
Routine Maintenance for Wire Brakes
Wire Brakes require some routine maintenance to keep them performing at their peak. Until you establish a history using a wire brake feature, a bi-weekly and monthly routine for maintaining your wire brake should be implemented as a preventative measure:
Bi-weekly Maintenance:
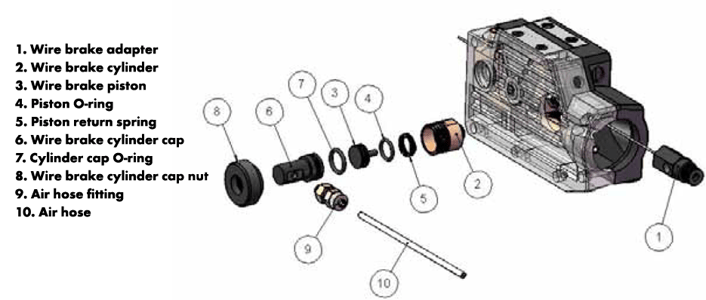
- Remove the wire brake cylinder from the wire brake adapter
- Inspect wire brake adapter and clean any shavings. Blow out the brake adapter with compressed air. Note that some through-arm mounting torch systems using a solid torch mount like iSTM or iCAT collision mounts require torch cable removal from the mount fro the wire brake adapter inspection.
- Remove and inspect cable wire liner and swanneck wire liner. Blow out the conduit and all liners with compressed air, and replace liners if necessary.
Monthly Maintenance:
- Disassemble the wire brake cylinder and the cylinder cap
- Inspect piston rod tip, piston return spring and O-rings, grease with O-ring grease and replace if necessary. Note that the piston rod tip should not be chipped or deformed
Common Wire Brake Problems in Robotic Welding
It is possible there will be issues you encounter outside of routine maintenance of your wire brake feature.
Here is a troubleshooting list of how to tackle the most common issues:
1. Wire is not holding steady
- If the cause is low air pressure, simply increase the air pressure (90 - 116 PSI recommended)
- If the air hose is kinked or damaged, inspect the air hose to free it or replace if necessary
- If the torch cable is too short and being stretched, adjust the wire feeder position or use a longer cable
- If there is an air leak detected, inspect everywhere air could be escaping. Check the valves, hose, fittings, and O-rings. Tighten where you can and replace components as necessary
- If there is damage to the piston tip, inspect the piston and replace as necessary
- If the wire size is incorrect, verify that the wire brake is designed for the wire size being used. Change the wire size or wire brake assembly to ensure they match up appropriately
2. Wire feed problem
- If there is insufficient piston return, then inspect the piston return spring. Also inspect the air hose and solenoid valve exhaust port functioning. Repair or replace as needed
- If the wire brake adapter and/or wire liner is clogged by wire shavings, clean the wire brake adapter and/or replace the wire liner
3. Erratic wire feed or wire shaving
- If the wire is feeding prior to the brake fully retracting, increase the wire feed delay or improve the air exhaust function via an air valve. This is the most common cause of wire shavings, which result in clogged brake adaptors and liners
- If the cable liner is sized incorrectly, inspect to verify then replace as necessary
A clean and properly functioning wire brake will prove a great tool for checking part placement and fit up on your welded parts. Keeping it maintained will reduce downtime and ensure that the most benefit is achieved from this small, but useful feature.
If you have any question regarding wire brake or any other ABICOR BINZEL Robotic Torch functions, please contact Product Support and be sure to check out additional items on our blog page.


