If a technically interested person opens a magazine or a newspaper you cannot avoid reading articles about how the “Internet of Things” will change our daily live in the coming years.
People in the industry know that this has already started. For those who aren’t sure of what it means, the Internet of Things (called IoT) or Industry 4.0 (the 4th industrial revolution) means that physical components (devices, machines, etc.) are connected to the Internet and with each other. Important is, what is so exciting about connecting devices and machines with the Internet: it allows getting real-time data about the processes that are running.
/Blog/Industry_4_0_Background.jpg?width=3875&name=Industry_4_0_Background.jpg)
These data can be used both by the costumer and the supplier: For a user of a device it is very interesting to know how often it is used, also compared to other devices, and to have an overview e.g. about productivity, savings, usage of resources and so on. For a supplier or a manufacturer it gives the possibility to survey the condition of the product or certain tools in the product, enabling things like predictive maintenance.
Shielding Gas & IoT
Gas Management creates a perfect storm for IoT product innovation. We are always asked how it is possible to save manufacturers on their use of shielding gas in a process like gas metal arc welding. For a mature technology you would expect that everything in gas management is already optimized, especially considering the fact that shielding gas contributes often a big part to the costs of a weld.
But as often happens, some aspects of arc welding have just been taken as a given: every welding machine uses a slow magnet valve; during weld breaks the magnet valves closes but does so slowly; and the gas flow is constant during a weld – even when the Amperage is changing.
These three facts were never before challenged. This caused us to ask if it could be improved upon. With that came the development of EWR – short for “Electronic Welding Regulator” and helps to control gas usage and allows gas savings in shielded gas metal arc welding of up to 60 %.
EWR and its patented technology uses a quick reacting frequency solenoid valve to take away the “start peak” of the gas flow and delivers directly a controlled gas flow, closes gas flow supply very fast when the gas post flow is over, and is synchronized the gas flow with the welding current.
This complete action ends up in total savings of up to 60% in shielding gas consumption, which has been proven in several thousand applications.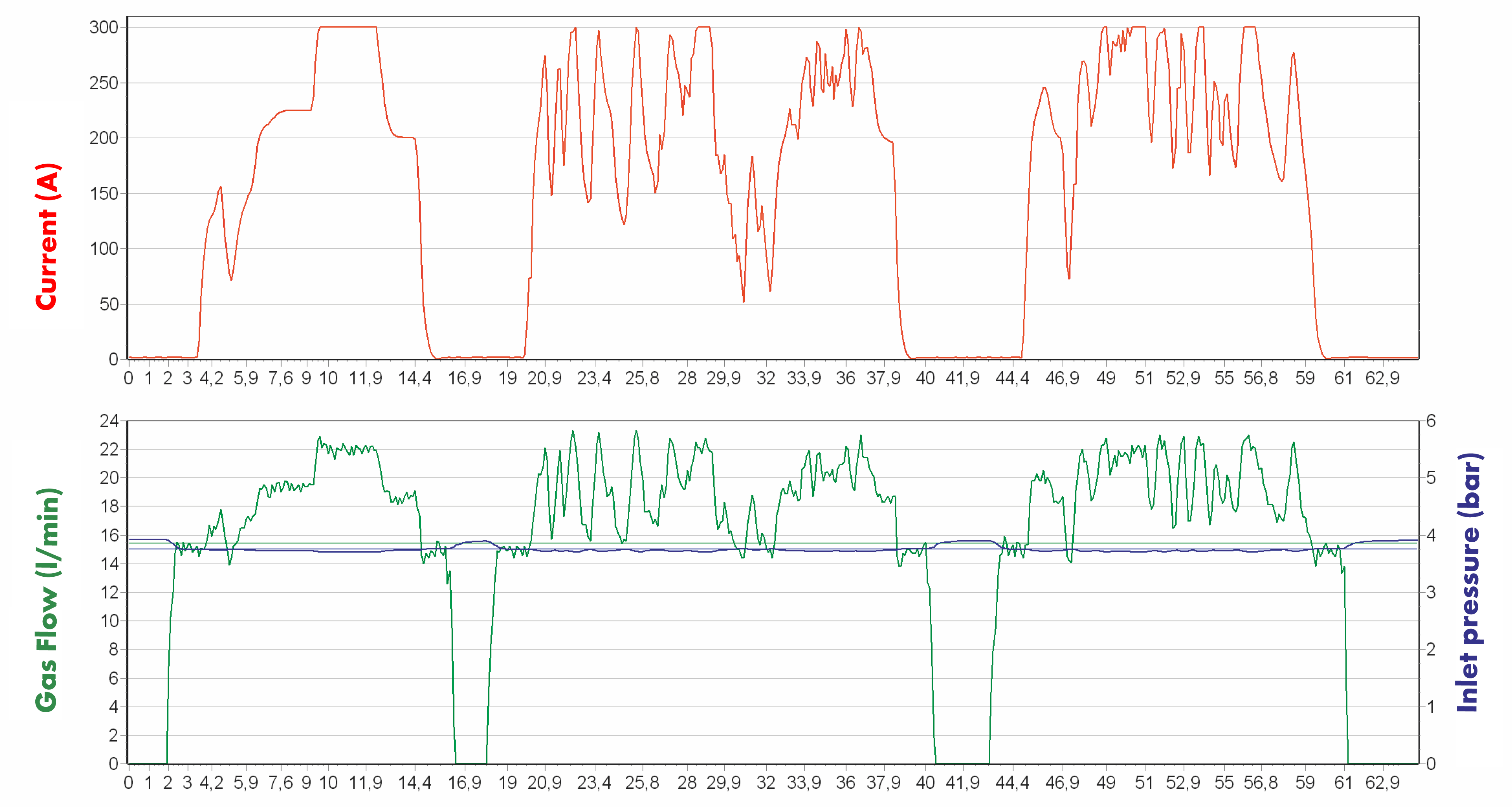
But there was more to a Gas Management System than just improving the manner in which gas was delivered. What is the next step? What does gas management for Industry 4.0 look like?
IoT in Today's Manufacturing Environment
Looking at IoT in a Gas Management System, today’s manufacturing environment has plenty of hardware devices that work to optimize or lessen or control gas flow through a manual intervention. What’s missing is a software that can interface into a local area network and be remotely managed. Think of being able to control everything about your Gas Delivery System from your desktop without having to physically be present with the device. Or how about having the ability to adjust gas type from CO2 to 98/2 Argon (or even a custom mix), then set your desired gas flow rate and bar setpoint remotely? Even from hundreds of miles away, by accessing a VPN or remote desktop you can adjust your gas delivery to account for different gas mixtures, delivery needs, and then being able to capture all of the gas usage data from that device, log it, and compare it to the weld station’s performance?
What if that software package can access tens or hundreds of these devices in your plant to fully capture your company’s entire gas use over a period of time to see where the inefficiencies lie?
This is Gas Management for Industry 4.0. A hardware with a software package that not only works to better deliver gas in relation to the weld current, but also allows the data from that hardware to be captured, aggregated, and analyzed?
We started to look into the topic also some time ago and are now proud to have our first IoT ready product: the EWR 2 Net, to address these very questions.
The Net-version can be connected to the Internet via a so-called field bus (we use a CAN open interface) or with an Ethernet interface (basically similar to the plug you use to connect your laptop to the internet). Now you can control all functions of the EWR 2 Net via the internet using the Service software. Not only set-up and adjustment is possible, but collecting the data about the achieved gas savings, used gas and welding current.
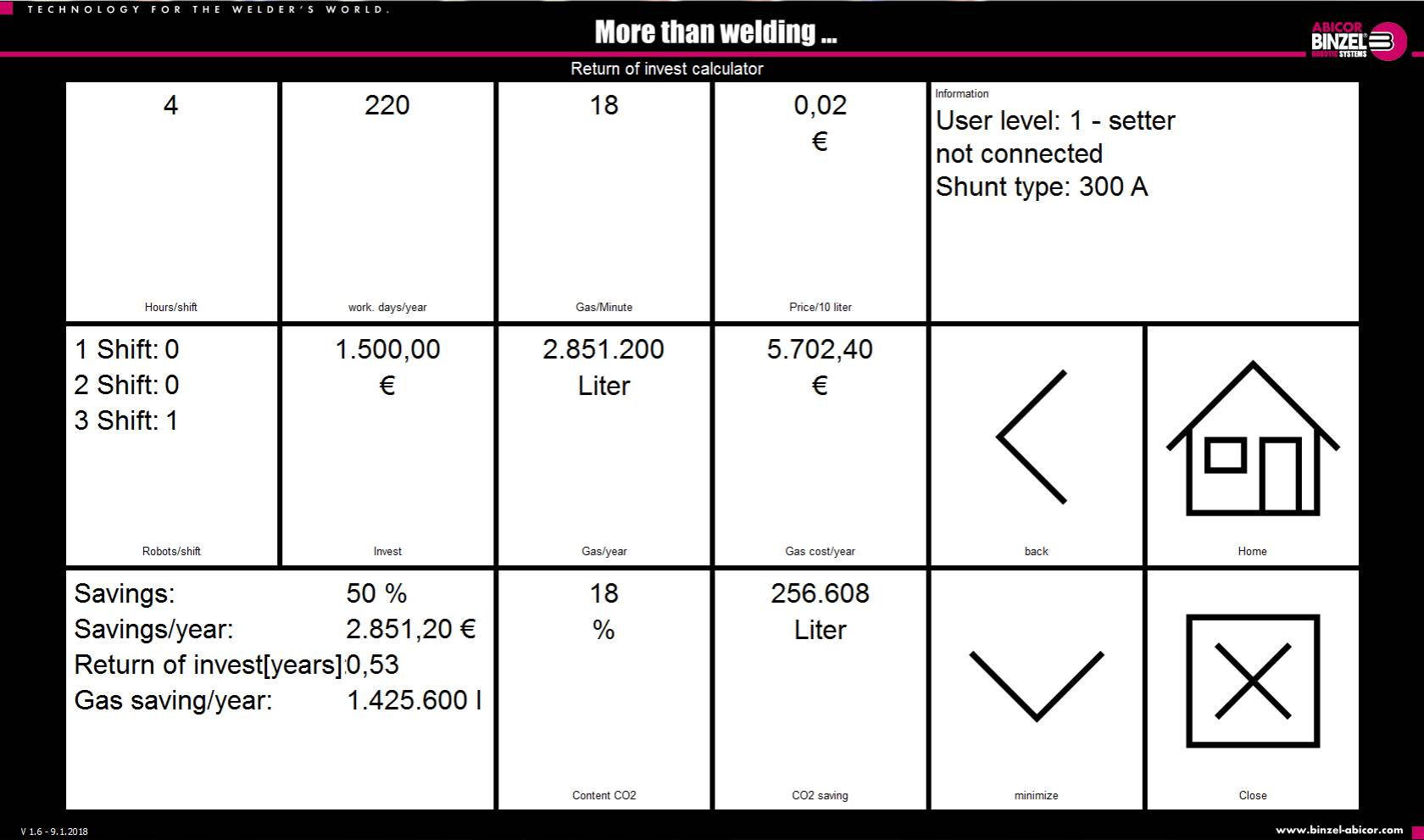
Using Argon/CO2 gas mixtures as in most applications there is an additional environmental benefit: saving shielding gas in this case also means reducing CO2 emissions. For one welding robot in 3 shift operation using an EWR can save up to 870 kg in CO2 every year. (Mixture with 18% CO2)
As welding demands more data and more predictive analytics to optimize efficiency and improve the cost of goods made, IoT will permeate more and more into all facets of welding and metalworking. What today is a simple software package tomorrow may be mobile applications, and then voice commands. While manufacturing learns to harness the power of Industry 4.0, the innovation of Industry 5.0 wait in the wings soon to follow.

